An electric valve is a valve that is opened and closed using an electric motor. Such valves are particularly well-suited to remote control of fluids such as aircraft deicing, farm irrigation, and automatic fire suppression. The most versatile valves used are the ball, butterfly, and gate valves, all of which are amenable to being motorized. The motor valve is also properly utilized, though, in systems that need incremental control of the valve as a system response to input. Manual inputs to valve actuation are the only difference between the two and their electric valve in internal mechanisms for fluid control.
Valves are components of fluid flow circuits in garden hoses and hydroelectric plants. Valve actuation would be challenging if the valves are distant or in inaccessible locations, too large to be opened or closed manually, or must be operated in a period when there are no crew operating facilities or installations. In all these instances, an electric valve is provided. Other than being powered by an electric motor, this type of valve acts exactly like a manual valve. This valve may be opened or closed remotely by a remote operator or an automatic system.
1. General Manufacturing Structure of Electric Valve
Electric actuators and valves make up the majority of electric valves. In electrical installations, actuators are powered by electricity. The connecting form of the stem nut and the connecting disc’s flange size comprise the output shaft, which facilitates the vertical displacement of the valve stem. The stem can operate the electric ball valve by causing the gate to move in a linear direction, thus enabling the valve to be opened and closed.
A manual operation mechanism is incorporated into the valve. In the absence of a power supply, manual operation is possible to open and close the valve. The valve can be closed when the handwheel undergoes a clockwise rotation. It is opened when the pneumatic ball valve rotates in the opposite direction of the cyclic motion.
The valve flange is constructed with a self-pressure sealing mechanism, and its sealing gasket is made of stainless steel metal, capable of withstanding 4500 pounds of high-pressure sealing. Reliance can be placed in the ball valve’s hermetic performance. A wedge single gate configuration is utilized for the gate. The construction of the valve is compact and diminutive.
The valve body is constructed using a forging and welding framework, effectively addressing the quality issues arising from casting defects, reducing waste generation, and enhancing product reliability. Gate and seat sealing materials were applied to the cobalt-based cemented carbide that had been affixed.
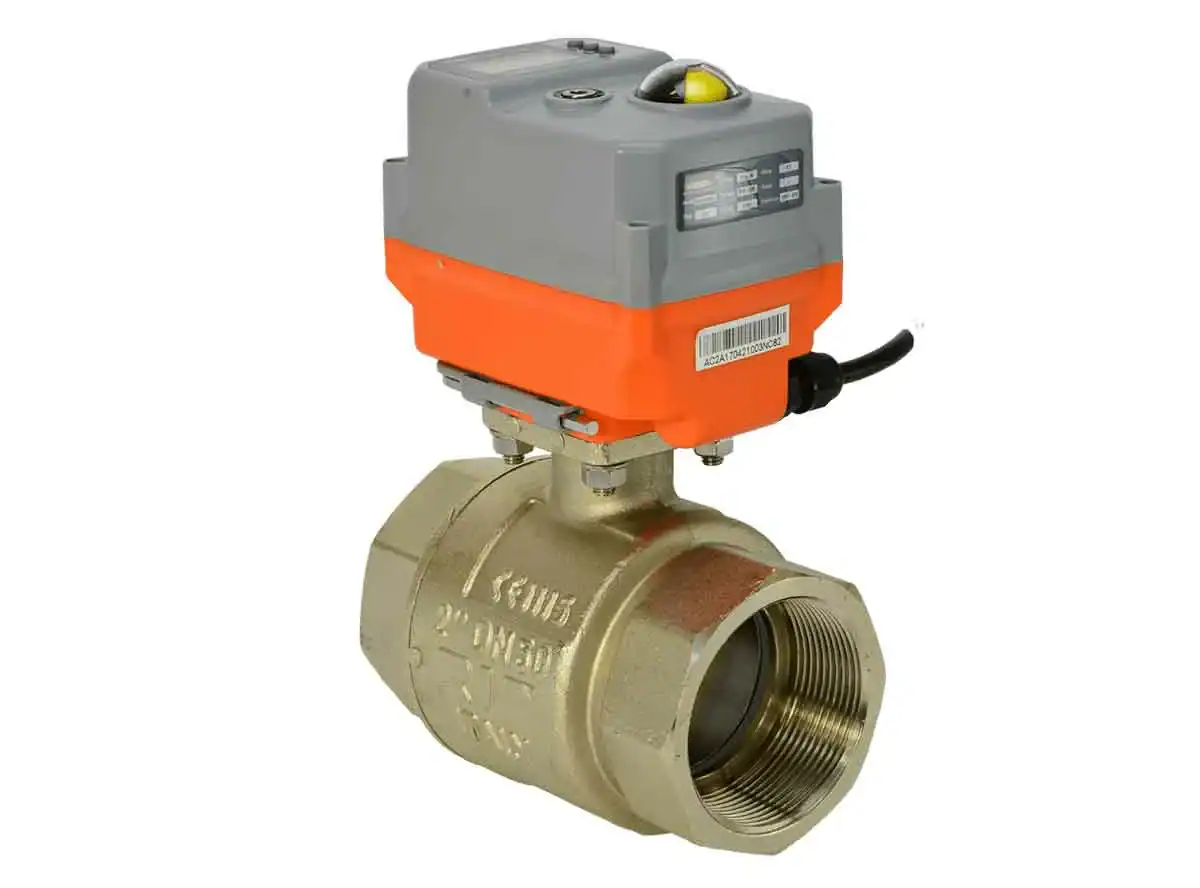

2. Manufacturing Components of Electric (motorized) Valve
When it comes to motorized(electric) valves, there are several common spare parts that you may need for maintenance or repairs. These include:
1) Body
The valve body is the valve assembly’s main structural component and primary pressure boundary. It acts as the seat against which the disc prevents fluid flow. It connects to the inlet and outlet piping via threaded, bolted, or welded connections and takes the bonnet via a threaded, bolted, or welded coupling. Forging or casting valve bodies is machined to interface with the other components.
2) Bonnet
Another significant pressure boundary component is the valve bonnet. It supports the disc, packaging, yoke/actuator, and stem, in addition to furnishing the closure head for the body. Connected to the valve body via threaded, mounted, welded, or pressure-sealed connections, bonnets are forged or cast. The connection between the bonnet and the valve body is a pressure boundary. Consequently, welds are classified as pressure boundary components.
3) Disc
The pressure boundary is completed by the valve disc, which also offers the capability to obstruct the flow path. Despite the disc being seated and the discharge piping depressurized, the entire system pressure is exerted. Discs are hard-faced and cast or forged to impart favorable wear characteristics.
4) Valve yoke
The valve yoke supplies the actuator with structural support. It always remains outside the pressure boundary and is connected to the valve body or bonnet. The yoke responds to the thrust or torque that the actuator applies to the valve stem.
5) Seats
Seats or seat rings serve as the disc’s sealing surface. In some designs, seat rings are omitted, and the body is machined as the sealing surface. In alternative designs, forged seat rings are threaded or welded to the body as a seating surface. Hard-faced is a common practice for sealing surfaces to enhance their wear characteristics. Seat rings are not classified as pressure boundary components because the body’s wall thickness is adequate to withstand the design pressure without their assistance.
6) Ball
The ball is pressed against the valve body and has a hole drilled through its center. It is attached to the valve stem, which is operated by the actuator. Whenever the actuator turns the stem, the ball is rotated to align the hole with the flow passage (open the valve and allow the flow of fluid) or shift the solid part of the ball to obstruct the flow passage (close the valve and shut off the flow). The ball is typically made of solid materials like metal or plastic.
7) Actuator
The actuator performs stem and disc assembly operations. Solenoid actuators, manual handwheels, manual levers, pneumatic actuators, or hydraulic actuators are all examples of actuators. Pressure boundary components do not include actuators, except specific hydraulically operated valves.
8) Stem
The stem of the valve converts the actuator’s motion to disc motion. Stems are forged and fastened to the disc via flexible joints or T-slots. The stem is held with a smooth surface finish in the area of the closure on valve designs that necessitate stem packaging or sealing to avert leakage.
3. How Does an Electric Valve Work?
Typically, electric actuators and valves connect to electric valves, which transform into electric valves during installation. The electric actuator is powered by electric energy through the electric valve to accomplish the toggling and regulating functions of the valve. To achieve the objective of modulating or altering the medium within the pipeline.
Motors are utilized to power electric valves. Adjustments can be made to the time required to execute the opening or closing action. Contrast with resist voltage shock. Electric valves operate at a higher switching frequency than solenoid valves, are typically employed in applications involving minimal flow and pressure, and have rapid opening and closing. The regulation of the electric valve’s release is possible. The valve’s states are half-off, on, and off. The solenoid valve cannot fulfill the requirement of controlling the passage of the medium in the pipeline.
A solenoid valve is classified as an electric valve; it pulls the valve core with the magnetic field generated by an electromagnetic coil, thereby modifying the valve body’s on/off state. In the absence of a coil, the valve core is reliant on the spring pressure to function.
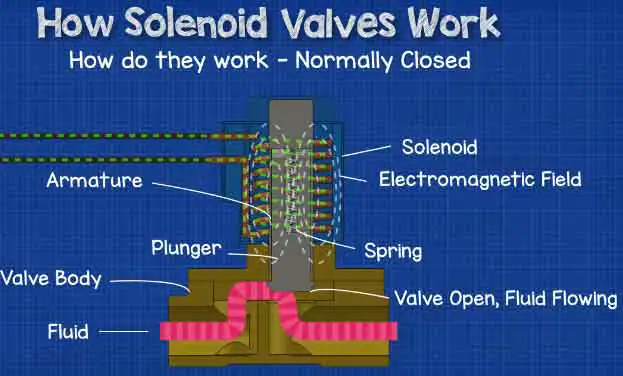
4. Applications of Electric Valves
Electric valves are an essential component of a wide range of industries, offering precise, automated liquid and gas control. By the conversion of electric signals into mechanical motion, electric valves offer efficient, effective performance in applications where it is impractical or wasteful to manually intervene. Electric valves are used in industrial production lines, complex HVAC systems, and city water mains, making processes easier, conserving energy, and improving overall system efficiency. Their reliability and accuracy make them priceless in modern fluid control operations.
1) Industrial Processes
Electric valves are frequently used in industrial settings, particularly in manufacturing, water treatment, and chemical processing, requiring precise and automated fluid flow regulation.
2) HVAC System
Electric valves are frequently employed in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems to regulate the passage of refrigerant or air precisely, thereby enhancing energy efficiency and temperature regulation.
3) Water Management
Electric valves also play a very critical role in water distribution and treatment networks by regulating the flow of water to various zones for accurate pressure regulation and distribution.
5. Factors to Consider When Choosing an Electric Valve
System requirements must be considered when choosing motor-operated valves for a given system. Pressure is one of the most crucial factors to consider. Without failure or malfunction, the valve must be capable of withstanding the utmost pressure of the system. Moreover, temperature becomes an imperative consideration, mainly when the fluid flow via the system is of a warm or cold nature. The valve must resist degradation or failure within the fluid’s temperature range.
Flow rate, which leads to the volume of fluid traversing the system in a given time, is a crucial factor to consider. The valve’s capacity should suit the system’s highest discharge rate. Refrain from paying attention to the account for these system prerequisites, which may give rise to a suboptimal functioning valve of an incorrect size, potentially culminating in the system’s failure.
1) Function of the valve (on/off, modulating)
When choosing an electric valve, one needs to check whether it is an on/off or modulating valve. On/off valves, i.e., valves that are meant to be fully open or closed, are best suited in systems that require on/off control, i.e., heating or cooling systems. Modulating valves, however, allow the starting or stopping of flow and are best suited for use in systems requiring flow control, i.e., hydronic heating systems.
It calls for a proper choice of valve function so that the valve can satisfy the control requirements of the system. Proper consideration of the valve function leads to a controlled system that is operating.
2) Media type (air, water, steam)
The second of the necessary factors in choosing a motor-operated valve is media type. The valve material must be compatible with the water, air, or steam transported by the system. Valves for various media have varying valve materials. For instance, valves for water systems must be corrosion-proof, while valves for steam systems must be high-temperature and high-pressure resistant.
Inappropriate choice of the material for the valve will result in leakage, early valve failure, and other faults that result in system failure. It is thus necessary to determine what material the valve will be most appropriate for regarding the medium the system will be conveying.
3) Valve material (brass, bronze, stainless steel)
One of the most significant factors to keep in mind while selecting a motor valve is the construction material of the valve. Valves are constructed of different materials, and every material possesses some advantages as well as disadvantages. For instance, brass valves possess corrosion resistance and high pressure-bearing capacity but should not be operated in alkaline or corrosive conditions.
Other than corrosion resistance and sea use suitability, bronze valves are not suitable for application in high-temperature systems. Stainless steel valves resist corrosion and high temperatures, and thus, they are suitable for fitting in steam systems. The choice of suitable valve material is very important to allow the valve to have the strength to be able to withstand the system demands without early failure.
6. Type of electric valve
A motorized valve actuator is a type of valve that closes and opens through the use of an electric motor. There are numerous other motorized valves with different characteristics and applications. A motorized form of valve is the ball valve. It regulates fluid passage through the rotation of a ball with a hole in the middle. The other is that the gate valve regulates fluid flow through a wedge-shaped disk or gate.
The third is the butterfly valve, a 90-degree rotating disc that throttles. The flow of very large quantities of fluids is controlled by the valves. The globe, diaphragm, and solenoid valves are motorized for precise control. The remaining specifications of the system to be controlled, i.e., fluid, pressure, temperature, and flow rate, determine the type of motorized valve to be utilized.
1) Electrical requirements (voltage, current)
In addition, while selecting, there is a need to consider the electrical requirements of the motorized valve. Motorized valves use an electric current to control them; therefore, the valve voltage and current ratings should be compatible with the electrical supply of the system. Failure to consider the electrical requirements can lead to an inoperable valve or destruction of the system’s electrical infrastructure.
For the valve to be in its most efficient state and without system damage, one with identical voltage and current ratings must be chosen. For any issue to be avoided, the manufacturer’s instructions must be followed while installing motorized valves with unique wiring arrangements.
2) Modulating vs On/Off Valves
There are two categories of electric valves: regulating and on/off valves. On/off valves provide a binary operation of either being wide open or closed. These are ideal for systems where close regulation is not required. The control valves provide precise control of flow by adjusting the valve position. They are thus ideal for process control and HVAC systems where precise flow is crucial. The choice to utilize either control valves or on/off valves is based on the needs of the system and the amount of control required.
7. How To Choose a Reliable Electric Valve Manufacturer?
Choosing the most reliable electric valve supplier when procuring an electric valve for a particular use is crucial. We always look for the fundamental wants and needs. Our aim must be to buy a product of reasonable price and quality. The factor of price is vital to every transaction.
1) Determine the product’s price
Endeavor to compare prices with competitors’ prices to choose the most affordable one. Concerning the policies and special offers, inquire. Our sole emphasis is on the quality of the product. These factors exert an influence on your enterprise. Since most valve manufacturers do not provide after-sales service, you must select the most suitable and optimal manufacturer to meet your needs. To choose the most reputable valve manufacturer.
2) Knowledge of the intended market
Electric valve manufacturers are prone to feeling more intimidated by prevalent quality concerns linked to their merchandise. They can meticulously manage and resolve the issues. Notably, most electric valve manufacturers specialize in producing a single product category or type.
When an electric valve supplier asserts that they manufacture a wide variety of products, they operate within the realm of trendsetting companies.
3) Quality of the product and reliability
Exactly what you need is a reputable manufacturer of valves. But having a good quality product should be your priority. Nobody likes to have products of inferior quality in this world. Good quality valves are a requirement for every buyer. Inspect the quality of the valves very carefully. A process that directs buyers to purchase samples from the original manufacturer and extensively inspects the valves. Conduct proper testing on your model to confirm its reliability and strength.
4) Valve maintenance assistance
Even correctly maintained valves may require repair in some circumstances. Consider a valve manufacturer that offers direct valve repairs on an extensive range of valves. Are members of the Valve Repair Council as well. While having work repaired, verify that the National Board for Repair Services accredits the manufacturer. Those valves bearing one of these labels will have their specifications restored to their initial state. Assess the manufacturer’s personnel regarding their industry expertise and factory training received directly from the valve producers.
5) Actuator service and sales
Select a company that possesses knowledge regarding the correlation between actuators and valves. Choose the manufacturer who can assist in product selection for your entire endeavor. Select the manufacturer of sophisticated pneumatic actuators that best meets the specifications of your application. Locate a manufacturer who provides services for actuators and valves and can direct you to the appropriate products.
6) Inventory on hand
How much inventory does the manufacturer carry? This number will have a direct impact on how long it takes to get your valves and components, which is vital in an emergency or unexpected breakdown. Working with a valve supplier that carries a large inventory will increase the chances that the required items will be available at the targeted time.
Regulatory incidents are quick, and industrial safety is a topic of prime concern near factories. Choose the valve manufacturer who complies with all safety standards, especially those that pertain to high-pressure valves, after a report brought to light a systemic deficiency in gas pipeline regulation. To make sure that your projects comply with all the relevant regulations, you need to select a valve manufacturer that has a history of showing a commitment to safety and proficiency in terms of the relevant standards.
7) Compare the Price with the Quality
Price and quality are the most influential and crucial factors when selecting the finest valve manufacturer for your industry. When pricing is exorbitant, sales frequently suffer, even when every other aspect is flawless. Therefore, investigate the price of each variety of valve. Assess whether the quality of the product justifies its price. Compare prices from various manufacturers to select the optimal valve supplier. However, be wary of con artists who offer discounted prices.
A practical approach to decision-making involves conducting a price comparison among various valve manufacturers. Begin the process by compiling a list of potential valves from manufacturers.
8) Valve warranty, guarantee policy
A warranty is a commitment made by the manufacturer to the consumer. It could ensure that you obtain the desired products and services. Confirm that the valve manufacturer offers a product warranty with customary terms and conditions.
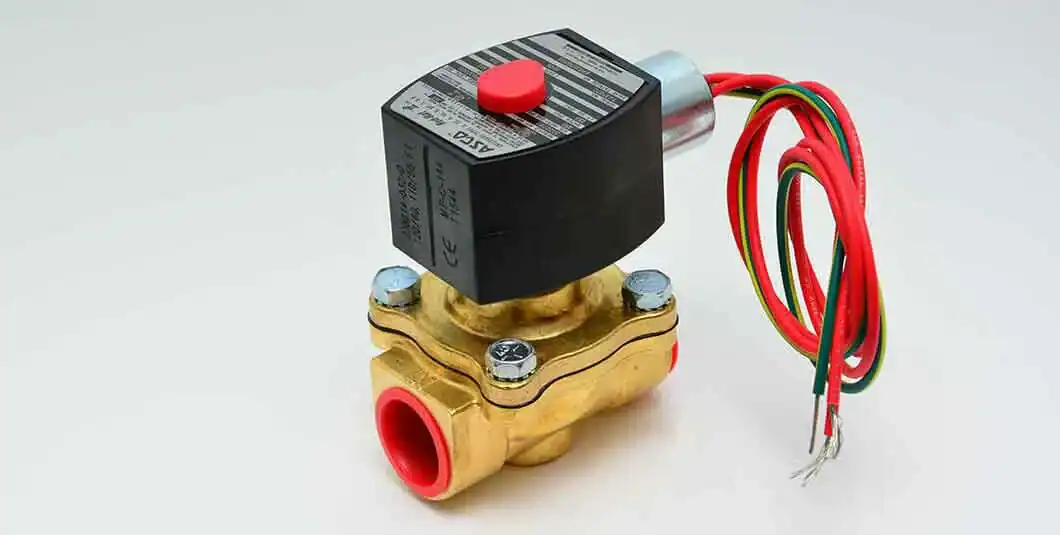

8. Electric Ball Valve Vs. Solenoid Valve
Both solenoid valves and electric ball valves are automated media control valves. The distinctions in their operations indicate which valve type is more suitable for specific applications. This comparison study examines the distinct characteristics that differentiate solenoid valves from electric ball valves to facilitate the choice between the two types of valves.
1) What Is A Solenoid Valve?
An electromechanical device, a solenoid valve comprises a coil encircling an actuator linked to a valve or seal mechanism. A magnetic field is produced when current passes through the coil; this field controls the closure or opening of the valve via the actuator. Consult our article on solenoid valves for additional details.
2) What Is An Electric Ball Valve?
An electric motor drives a ball within the interior of an electric ball valve. A port is located in the center of the spheroid. Upon the valve opening, the alignment of the ball’s port with the inlet and outlets facilitates fluid passage through the valve. The body of the ball blocks flow through the valve when closed, resulting in the port being perpendicular to both the inlet and outlets.
Electric ball valves generally require a minimum of two to three seconds and sometimes an extended duration when moving from a closed to an open position. Due to their virtually instantaneous operation, solenoid valves are the superior choice for applications that need an exceptionally rapid response time from the valve. Examples include applications involving compressed air, heating, and car washes. Flow rates are more significant with electric ball valves than with solenoid valves. Several variables, including the type of valve, the pressure drop, and the Kv factor, determine the flow rate.
Electric ball and solenoid valves are designed to control on/off. However, a design option exists for each form of valve to achieve more precise flow regulation. Read up on proportional solenoid and v-port ball valves to gain further insight.
Electric ball valves are significantly more effective than solenoid valves at handling media containing microscopic particles. A solenoid valve is susceptible to rapid clogging by particles, whereas the movement of the ball valve across its seat tends to expel particles. Consult the manufacturer’s manual of the valve for additional information regarding the utmost particle size and whether a filter is necessary in front of the valve for a given application.
The power consumption of solenoid valves is greater than that of electric ball valves. More power is typically required to maintain the energized state of a solenoid valve compared to the power needed to open or close the valve. However, electric ball valves solely necessitate power for opening and closing, with no power requirement for valve maintenance. However, there are designs of solenoid valves that can remain in that position without the need for power. For more information, consult our article on latching solenoid valves.
When deactivated, solenoid valves are either open or closed. When a malfunction occurs, such as an electrical outage, these valves will remain immobile in the de-energized state. The user can use this information to determine whether the valve should be closed or opened in case of a malfunction. Usually, electric ball valves lack this capability.
Solenoid valves cannot withstand higher pressures than ball valves, particularly high-pressure ones. Ball valves designed for high-pressure applications can withstand up to 700 bar (10.000 psi). Conversely, an indirect-acting solenoid valve designed for high pressure is limited to operating at a maximum of 90 bar (1300 psi). Indirect-acting solenoid valves can manage pressures of up to 16 bar (232 psi).
Electric ball valves are considered superior when the diameter is 50 mm (2 inches). Additionally, when choosing a solenoid valve between 50 mm and 12.7 mm (0.5 inches) in size, opt for a semi-direct or indirect solenoid valve rather than a direct-acting one. Direct-acting solenoid valves function solely on the magnetic force generated by the solenoid. Consequently, solenoid dimensions that exceed 12.7 mm in diameter precipitate astronomical costs.

9. Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Valve
Motorized valves may also produce noise when operating, an additional potential drawback. Distracting from other activities or conversations, this commotion may cause difficulty for individuals. Occasionally, the noise level could be sufficiently high to induce auditory impairment.
1) Advantages of Electric Valve
The primary benefit of electric valves is that they can control the flow of fluids in a system with the highest possible precision and accuracy. Processes could be intricate in numerous adjustments to get the preferred outcome, and I find this to be particularly useful. In addition to preventing human error, motorized valves work automatically and give consistency in performance.
Moreover, these valves are more energy efficient than manual valves since they are only activated.
Further, rotary valves are more flexible to accommodate varying media or operating pressures compared to manual valves. In addition, they are usually capable of being coupled with systems that are already in place seamlessly, so they can start operating right away and without interfering with production operations.
Electric valves are more precise than manual valves. Remote operation of electric valves is handy in most applications.
They are available in various materials, including brass, plastic, and stainless steel. They are utilized in low-pressure as well as high-pressure applications. Chemical, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage industries are some industries that utilize them.
2) Disadvantages of Electric Valve:
A second drawback that is associated with motorized valves is the possibility of detection trouble. Because they are typically only sold at specialty plumbing or hardware stores, people looking for them may be required to find them through wholesale distributors or manufacturers that specialize in them.
With motorized valves, there can be electrical problems in some homes or businesses. A power loss prevents the valve from opening or closing, and it can cause problems. Also, if the power connection is disrupted while operating the valve, it can become jammed in that particular state.
10. Comparison Between an Electric Valve and A Pneumatic Valve
The intended application is also an important consideration while deciding between electric and pneumatic valves. Low to medium pressure operations are suitable for pneumatic valves, whereas high-pressure operations are better suited to electric valves. Electric valves find typical uses in gas, steam, and other media that demand precise control and quick response times.
1) Operation
Pneumatic valves regulate the flow of fluids or gases through compressed air or gas; however, an electric current powers electric valves. Since an external source powers the electric valve, it is most suitable for sites with a consistent power grid. In contrast, pneumatic valves are more affordable and easier to install; however, they need an air compressor.
2) Accuracy and speed
In addition to regulating gas or fluid flow in real-time, electric valves are more precise and quicker than pneumatic valves. In addition, for more accurate and rapid regulation, electronic valves may be integrated with programmable logic controllers (PLCs). In contrast, due to their reliance on air pressure, pneumatic valves operate more slowly than their electric counterparts and require better precision.
3) Environment
Electric valves are not preferred when operating in unsafe environments, such as chemical facilities that handle corrosive substances. Pneumatic valves are the preferred choice. This is because pneumatic valves do not generate electrical charges that could cause corrosion or ignition. Electric valves have the potential to generate sparks, which may result in electric shocks that are perilous and could inflict harm.

11. Raw Materials Used in Electric Valve Manufacturing
As it determines the valve’s performance in particular environments and circumstances, selecting material is critical in industrial valve production. In consideration of various performance criteria and applications, a variety of materials are frequently employed.
1) Ductile Iron
The composition of ductile iron is comparable to cast iron, but it is more flexible and robust. This material is highly resistant to high-pressure and high-stress environments, making it highly suitable for oil, gas, and waterworks.
2) Cast Iron
Industrial valve manufacturing frequently employs cast iron, a strong and economical material. It is highly versatile for low-pressure applications in water, steam, and gas, and is an ideal choice for general-purpose applications in most industries.
3) Carbon Steel
Due to its resistance to high temperatures and its excellent strength, carbon steel is a widely used material in the valve manufacturing sector. Due to its resistance to wear and strain, this material is applied in high-temperature and high-pressure operations, such as those found in the oil refining and power generation sectors and regions, including the United States and Saudi Arabia.
4) Stainless steel
Corrosive fluids, chemicals, and environments subject control valves, which are constructed from stainless steel, to be non-reactive and highly resistant. Their high resistance to corrosion as well as non-reactivity, is utilized in the food processing, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries.
5) Brass
Brass is employed in the fabrication of industrial valves owing to its exceptional machinability and resistance to corrosion. It is highly suitable for water and petrochemical applications at low to medium pressure. Plumbing systems and other residential and commercial applications incorporate brass.
12. Quality Control Measures in Electric Valve Manufacturing
Integral to the industrial valve manufacturing process, quality control makes sure that the final product conforms to all applicable standards and specifications. Manufacturers of industrial valves implement a variety of quality control procedures, including:
- Raw material inspection
- Inspection of the manufacturing process during machining and assembly
- Defect detection and performance evaluation via pressure testing
- Finishing inspection and quality assurance before shipment
These protocols ensure that the manufactured valves are of optimal quality and will operate effectively in their designated uses.
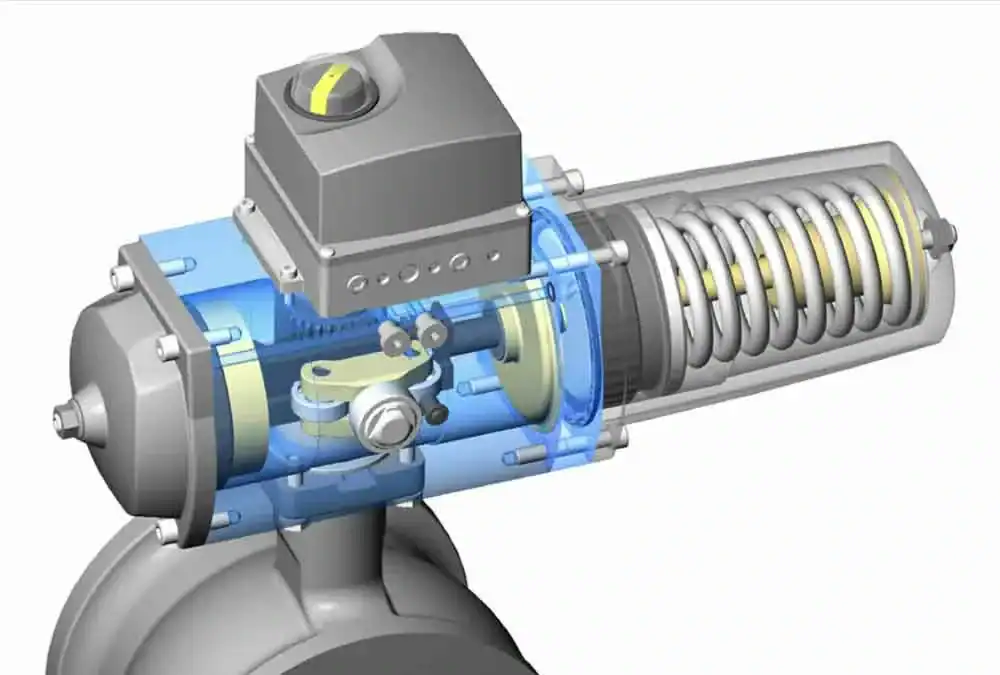
13. How Does a (Valve) Actuator Work?
Electric valve actuators control a valve opening or closing. They are compatible with various valve types, such as ball and butterfly valves, and can generate either linear or rotary motion. Electric valve actuators are vital for assisting closed or dispersed systems over a large area, as they respond to commands via remote control or centralized process control systems. By controlling electric actuators from a centralized system with programmed and organized instructions, process control systems enable businesses to automate the system and increase its reliability.
14. Why Choose Plumberstar?
“Safe pair of hands.” We are one of the leading valve suppliers in China, owing to our combined decades of experience. Without exception, our pricing strategy is to provide exceptional value. We do not offer low-quality valves with components that wear out quickly. We provide excellent quality, safety, and durability valves with outstanding technical and consulting services. Customers obtain valves at competitive prices with quality-checked and certified to globally recognized standards due to our considerable purchasing power and extensive experience. We provide a valuable consulting service that includes free on-site surveys with no obligation.
Our parts suppliers are selected from the most reputable manufacturers around the globe, prioritizing quality. They have also undergone audits by our agents and hold ISO 9001 certification.
